The Second Amendment to the United States Constitution, ratified in 1791, is a fundamental right that has sparked intense debate and controversy over the years. It reads:
“A well regulated Militia, being necessary to the security of a free State, the right of the people to keep and bear Arms, shall not be infringed.”
This brief but powerful statement has been subject to varied interpretations, shaping American legal and political landscapes. This article explores the historical context, landmark Supreme Court cases, ongoing political debates, and the broader implications of the Second Amendment in modern American society.
Online Casinos are deeply rooted in American culture due to the nation’s long-standing tradition of entertainment, risk-taking, and the pursuit of fortune. From the early days of riverboat gambling in the 19th century to the glittering casinos of Las Vegas and Atlantic City, they have symbolized a spirit of adventure and escapism.
Historical Context
The origins of the Second Amendment lie in the historical context of post-revolutionary America. The Founding Fathers, wary of a standing army and centralized power, emphasized the need for a well-regulated militia to ensure the security of a free state. This perspective was influenced by English common law and colonial experiences with militias.
English Common Law Influence

The right to bear arms has a rich history that dates back to the English Bill of Rights of 1689. This document, which was a crucial part of the English constitutional settlement following the Glorious Revolution, explicitly stated that Protestants had the right to possess arms for their defense, as long as these arms were suitable to their conditions and in accordance with the law.
The English Bill of Rights was a significant milestone in the development of the right to bear arms, as it built upon the existing common law tradition and reflected the specific circumstances of the time. The Bill of Rights was enacted in the aftermath of the Glorious Revolution, which had seen the overthrow of the Catholic King James II and the establishment of a Protestant monarchy under William III and Mary II. The right to bear arms was seen as a crucial aspect of the new constitutional order, ensuring that Protestants could protect themselves from potential Catholic threats.
The influence of the English Bill of Rights on the development of the right to bear arms in other jurisdictions, particularly in the United States, is significant. The Second Amendment to the United States Constitution, adopted in 1791, explicitly guarantees the right to keep and bear arms, citing the English Bill of Rights as a key precedent. The historical connection between the English Bill of Rights and the Second Amendment underscores the importance of the right to bear arms in the English common law tradition and its subsequent impact on the development of constitutional rights in other countries.
Colonial Militias
During the colonial period, militias were essential for defense against external threats and internal insurrections. The experience of arming citizens to form militias influenced the Founders’ thinking. The fear of a standing army, seen as a potential tool for tyranny, further underscored the need for an armed citizenry.
Supreme Court Interpretations
The Supreme Court has played a pivotal role in interpreting the Second Amendment, particularly in the last few decades. Two landmark cases, District of Columbia v. Heller (2008) and McDonald v. City of Chicago (2010), have significantly shaped contemporary understanding of this constitutional right.
District of Columbia v. Heller (2008)
In District of Columbia v. Heller, the Supreme Court ruled that the Second Amendment protects an individual’s right to possess a firearm, unconnected with service in a militia, and to use that arm for traditionally lawful purposes, such as self-defense within the home. This decision marked a departure from the earlier collective rights interpretation, emphasizing individual rights instead.
Key points from the Heller decision include:
- Recognition of an individual right to bear arms.
- Affirmation that the right is not unlimited and can be subject to regulations.
- Emphasis on the historical context of self-defense.
McDonald v. City of Chicago (2010)
Following Heller, the McDonald v. City of Chicago case extended the Second Amendment’s protections to the states through the Fourteenth Amendment. This ruling ensured that state and local governments could not infringe upon the individual right to keep and bear arms.
Key aspects of the McDonald decision include:
- Application of the Second Amendment to state and local laws.
- Reinforcement of the individual right to bear arms for self-defense.
- Recognition of reasonable regulations consistent with this right.
Political and Ideological Debates
The Second Amendment remains a deeply polarizing issue in American politics. Organizations like the National Rifle Association (NRA) and advocacy groups for gun control represent the spectrum of opinions on gun rights and regulations.
The National Rifle Association (NRA)
The NRA has been a powerful advocate for gun rights, emphasizing the Second Amendment as a safeguard against government tyranny and an essential component of individual liberty. Their lobbying efforts have significantly influenced gun legislation and public opinion.
NRA’s core arguments include:
- The Second Amendment as an individual right.
- Opposition to restrictive gun control measures.
- Promotion of gun ownership for self-defense and recreational purposes.
Gun Control Advocacy
On the other side of the debate, numerous organizations and individuals call for stricter gun control measures to address the growing problem of gun violence in the United States. They argue that reasonable regulations are necessary to ensure public safety and reduce incidents of mass shootings and everyday gun violence.
Key arguments for gun control include:
- The need for comprehensive background checks.
- Restrictions on the sale of high-capacity magazines and assault weapons.
- Implementation of red flag laws to prevent individuals deemed dangerous from accessing firearms.
Legal Challenges and Controversies
The Second Amendment has been at the center of numerous legal challenges and controversies. Recent Supreme Court decisions continue to shape the legal landscape surrounding gun rights and regulations.
Second Amendment Sanctuary States
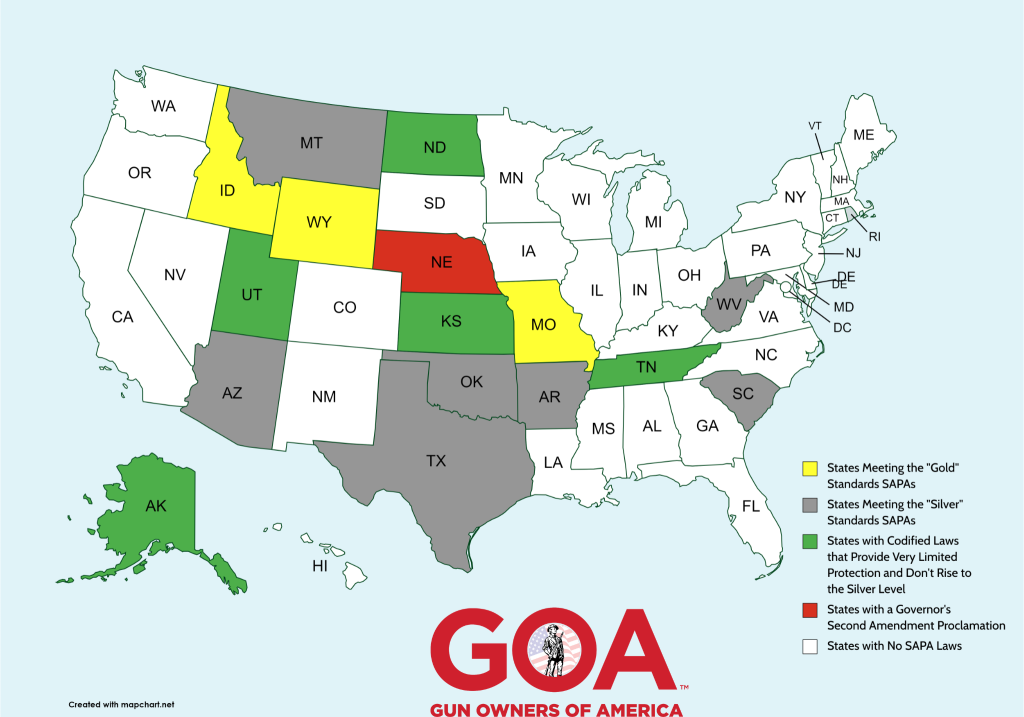
This is a is a visual representation of the Second Amendment Sanctuary States (SAPAs) in the United States. The map categorizes states based on the level of protection they provide for gun owners against gun control measures that violate the Second Amendment.
New York State Rifle & Pistol Association, Inc. v. Bruen (2022)
In the 2022 case of New York State Rifle & Pistol Association, Inc. v. Bruen, the Supreme Court struck down New York’s century-old public carry licensing law, which required applicants to demonstrate a specific need for carrying a firearm in public. This decision established a new framework for evaluating Second Amendment challenges, emphasizing that the right to carry a firearm in public for self-defense is constitutionally protected.
Implications of the Bruen decision:
- Increased scrutiny of state and local gun regulations.
- Expansion of the individual right to carry firearms in public.
- Potential for more legal challenges to existing gun control laws.
The Broader Implications of the Second Amendment
Despite the ongoing debates and controversies, the Second Amendment holds significant importance in American society. It is seen by many as a fundamental right essential to the security and freedom of the American people. However, balancing this right with public safety concerns remains a complex and contentious issue.
Gun Violence in America
Gun violence is a pressing issue in the United States, with high rates of firearm-related homicides, suicides, and mass shootings compared to other developed countries. The debate over the Second Amendment often intersects with discussions on how to effectively address this public health crisis.
Statistics on gun violence:
- The United States has one of the highest rates of gun ownership and gun-related deaths in the world.
- Firearm-related deaths are a leading cause of death among children and teenagers in America.
- Mass shootings have become more frequent, prompting calls for stricter gun control measures.
Public Opinion and Legislative Efforts
Public opinion on gun rights and regulations is deeply divided. While a significant portion of the population supports the right to bear arms, there is also widespread support for certain gun control measures. Legislative efforts at the federal and state levels reflect these divisions, with varying degrees of success in enacting gun-related laws.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
Advances in technology and innovation in firearms have also impacted the Second Amendment debate. The development of 3D-printed guns, smart gun technology, and the proliferation of semi-automatic and automatic weapons pose new challenges for regulation and enforcement.
Conclusion
The Second Amendment to the United States Constitution is a cornerstone of American law and society, representing a right that is both fiercely defended and hotly contested. Its interpretation has evolved over time, shaped by historical context, Supreme Court rulings, and ongoing political and ideological battles. As the nation continues to grapple with issues of gun violence and public safety, the debate over the Second Amendment remains as relevant as ever.
Understanding the complexities of this constitutional right requires a nuanced appreciation of its historical roots, legal interpretations, and the diverse perspectives that shape its role in contemporary America. As the conversation continues, finding a balance between individual rights and collective safety will be crucial in addressing the challenges and opportunities presented by the Second Amendment.
References
For more detailed information on the Second Amendment and related topics, you can explore the following resources:
- Valparaiso University Law Review
- Giffords Law Center on Second Amendment Challenges
- Bridgewater State University – Guns, Violence, and the Second Amendment
- Justia – Supreme Court Gun Rights Cases
- Britannica – Second Amendment: Origins and Historical Antecedents
- NRA Institute for Legislative Action – What is the Second Amendment and How is it Defined?
- Cornell Law School – Second Amendment
- Gun Owners of America – Second Amendment Sanctuary States
